Optimizing energy efficiency in IoT networks for sustainable smart cities: a focus on energy-efficient communication protocols
Keywords:
Energy-efficient IoT protocols, Smart city sustainability, Hybrid energy harvestingAbstract
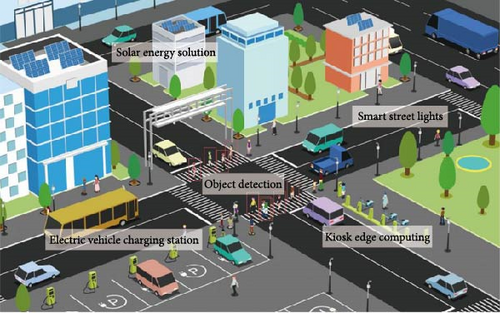
The rapid expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) is driving the development of smart cities by improving connectivity and automation. However, the increasing number of IoT devices raises concerns about energy consumption, device longevity, and network sustainability. High energy demands lead to higher costs and limit large-scale deployments. To address these issues, energy-efficient protocols are essential for optimizing power consumption while maintaining network reliability. Key strategies include adaptive power control, duty cycling, and hybrid energy harvesting. The Hybrid Energy Harvesting-Based Energy Neutral Operation Medium Access Control (HENO-MAC) protocol integrates solar and wind energy to support energy-neutral operations. Additionally, advanced Medium Access Control (MAC) and routing protocols, such as the Routing Protocol for Low-Power and Lossy Networks (RPL), help minimize energy wastage. Emerging communication standards like Thread 1.4 further enhance energy efficiency and security. This study evaluates state-of-the-art energy-efficient IoT protocols in smart urban environments, analyzing technologies such as (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) MQTT, RPL, and Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP). It also explores AI-driven energy management, edge computing, and energy-harvesting IoT systems. Through case studies from smart city initiatives in Barcelona and Singapore, the research highlights best practices for improving sustainability in IoT-driven cities.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Nubunga Ishaya, Hakeem Adewale Sulaimon, Hadiza Abdullahi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




