Copper catalysis the synthesis of functionalized glycine-based sulphonamides: In silico and in vitro antibacterial studies
Keywords:
Copper , N-arylation , Functionalized , Sulphonamides glycine, In silico studiesAbstract
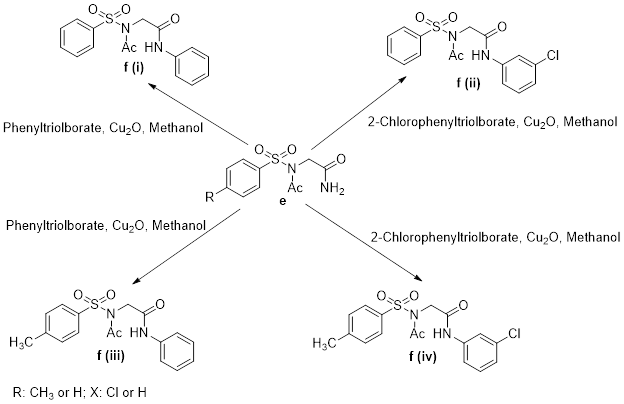
The synthesis of functionalized glycine-based sulphonamides via copper catalyzed N-arylation reaction and the in silico, in vitro antibacterial studies is reported. The procedure involved the initial synthesis of substituted p-toluenesulphonamides and substituted benzenesulphonamides by the reaction of glycine with p-toluenesulphonyl chloride and benzenesulphonyl chloride respectively in aqueous basic medium. The syn[1]thesized compounds were acetylated by reacting them with acetic anhydride and sodium acetate followed by acylation and amidation to yield amidated p-toluenesulphonamides and benzenesulphonamides respectively. Copper catalyzed N-arylation of the amidated products with aryltriolborates resulted in the synthesis of benzene, and 2-chlorophenyl derivatives of the amidated products. The synthesized compounds were characterized using FTIR, 1HNMR and elemental analysis and the spectra were in agreement with the assigned structures. The in silico antibacterial studies revealed that the compounds possess significant antibacterial potency in the respective bacteria cells and could be further employed as potential anti-bacterial agents. The in vitro antimicrobial study revealed that most of the synthesized compounds possess antibacterial activities.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2024 A. D. Jacob, U. C. Okoro, A. J. Dauda

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







